You've may have put many new filters on your car when changing the oil, but have you ever noticed inside one? Take a view at the basics of an oil filter.
- Posted 5 years ago
- 1313 Views
An
oil filter is an essential component in your vehicle and it plays very
important role which cannot be underestimated. An oil filter removes all the
debris and contaminants. This ensures that the engine is supplied with clean
oil at all times.
Oil filters are key
components to engine performance and durability.
Health and life of the major components of the engine are dependent on the
quality of oil delivered to them. Contaminated
oil might lead to the failure of some of the engine's components. Such oil can
also lead to high costs of repairing the engine as some of the parts might
require being replaced. High-quality oil should be transferred through the
vehicle's engine.
Oil filters plays a
very important role and if your oil
filter has poor quality, it can shorten the life of your engine and
cause other parts to fail as well. The oil filter cleans the oil as
it passes through the filter and prevents abrasive
contaminants from damaging the parts in the engine.
Using
the poor or low quality oil filter can negatively impact oil pressure.
That will not work properly, or a filter that gets clogged can
cause oil pressure to drop. If the relief
valve is damaged, or the wrong filter is used, too much or too
little oil can pass into the engine. To maintain the effectiveness and quality of your car engine
shop with ZENITH FILTERS, a leading exporter and manufacturer of all kinds of
filters.
ZENITH filters design and manufacture high quality automotive filters using
the best production line and updated technology and meet the requirements of
the specified vehicles.
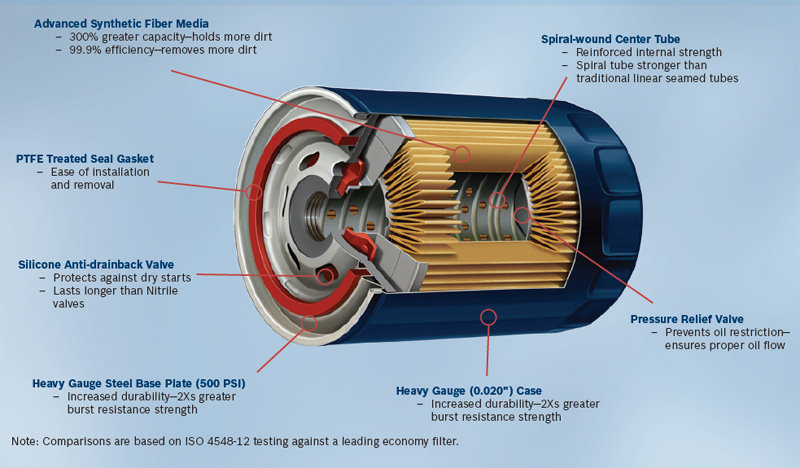
1. TAPPING PLATE
This serves as the entry and exit point
for oil. Small holes around the edge facilitate the free flow of oil into the
container. The threaded center hole is where the oil flows out and also how the
container attaches to the engine.
2. ANTIDRAINBACK VALVE
Because the oil filter is typically
located toward the middle or bottom of an engine, this rubber valve has a flap
that blocks oil from draining back into the filter when the engine is off.
3. FILTER MEDIUM
The porous filter medium consists
primarily of microscopic cellulose fibers along with synthetic fibers such as
glass and polyester, which increase filtering efficiency and durability. The
medium is also saturated with resin to give it strength and stiffness.
Higher-grade filters have more synthetic fibers.
4. PLEATS
Folding the filter medium creates a
greater total surface area. The number of pleats depends on the medium's
thickness.
5. CENTER STEEL TUBE
The center tube provides structure and
lets filtered oil return to the engine. The number, size, and position of the
holes is key to ensuring that the oil flow is not restricted.
6. RELIEF VALVE
On a cold startup, oil can be too thick
to filter. To prevent the engine from starving, the relief valve opens when the
pressure builds enough to force the calibrated spring downward, allowing
unfiltered oil into the center tube through the top.
7. END DISC
To keep unfiltered oil from leaking
into the center tube, a fiber or metal end disc is bonded to each end of the
filter medium. Some brands forgo discs and use a sealant to create solid ends.
8. RETAINER
A thin bit of metal that acts as a leaf
spring, the retainer keeps the filter medium and end disc tight against the
tapping plate.
Oil filters
extract particles created in the lubrication flow: metal particles, combustion
particles, and dust, which could damage and wear the engine.